Offset printing remains the industry standard for high-volume, high-quality commercial printing projects. This printing technique involves transferring an inked image from a plate to a rubber blanket before applying it to the printing surface. The term “offset” refers to this indirect transfer method, where the image is not directly applied to the paper.
When clients ask “what is offset printing,” we explain it’s the preferred method for high-quality, large-volume print jobs. The technique relies on the basic principle that oil and water don’t mix, creating a chemical process that produces exceptional print quality. Understanding what is offset printing helps businesses make informed decisions about their printing needs, especially when quality and quantity are primary concerns.
The history of offset printing dates back to the late 19th century, with significant commercial adoption occurring in the early 20th century. Since then, it has evolved to become the dominant printing method for magazines, books, newspapers, packaging, and marketing materials worldwide.
Offset Lithography: The Foundation of Modern Printing
The principles of offset lithography rely on the repulsion between oil and water to create crisp, clean images. In this process, the printing plate contains two types of surfaces: image areas that attract oil-based ink and repel water, and non-image areas that attract water and repel ink.
Modern offset lithography has evolved significantly since its invention in the early 20th century. The fundamental concept remains unchanged, but technological advancements have improved efficiency, quality, and versatility. Understanding offset lithography is essential for anyone working in the printing industry, as it forms the foundation for most commercial printing operations.
Offset lithography printing produces exceptional results for projects requiring precise color reproduction. The versatility of offset lithography printing makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from fine art reproduction to commercial packaging. For premium marketing materials, offset lithography printing delivers unmatched quality and consistency that digital methods often struggle to achieve.
Offset Printing Process: How It Works Step by Step
The offset printing process begins with creating plates that separate the image into individual color components. Each plate corresponds to one of the four process colors: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (CMYK). For specialty colors, additional plates may be created.
Here’s a breakdown of the complete offset printing process:
- Pre-press preparation: The design is converted into printing plates through a photochemical or direct-to-plate process.
- Plate mounting: Each aluminum plate is mounted on a cylinder in the printing press.
- Dampening: The plate is moistened with water, which adheres to the non-image areas.
- Inking: Oil-based ink is applied, which adheres only to the image areas of the plate.
- Transfer to blanket: The inked image transfers from the plate to a rubber blanket cylinder.
- Impression: The blanket cylinder transfers the image to the paper as it passes between the blanket and impression cylinders.
- Drying and finishing: The printed sheets are dried and undergo finishing processes like cutting, folding, or binding.
Quality control throughout the offset printing process ensures consistent results across the entire print run. Mastering the offset printing process requires both technical knowledge and practical experience, which is why established printing companies often produce superior results.
How Offset Printing Works: The Technical Mechanism
To understand how offset printing works, you need to grasp the principle of indirect transfer using plates and blankets. This method creates a sharper, cleaner image than direct printing methods because the flexible rubber blanket conforms to the texture of the printing surface.
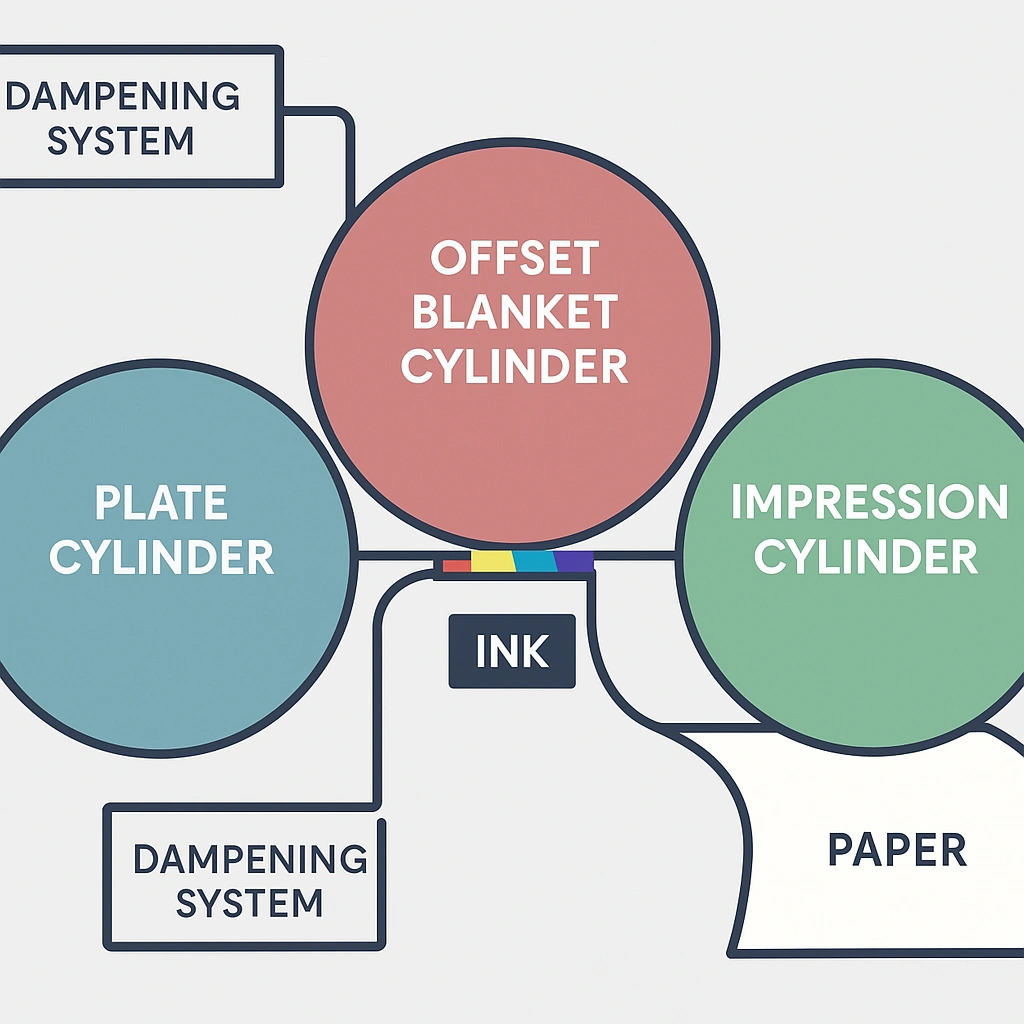
The science behind how offset printing works involves the natural repulsion between oil-based inks and water. The printing plate is first dampened with water, which adheres to the non-image areas. When ink is applied, it’s repelled by the water and sticks only to the image areas. This inked image transfers to the rubber blanket and then to the paper.
Learning how offset printing works helps designers create files that produce optimal results. Understanding the technical aspects of the process allows for better color management, appropriate image resolution, and proper file preparation. This knowledge is particularly valuable when designing materials that require precise color matching or special printing effects.
Offset Printing Press: Components and Technology Explained
A typical offset printing press consists of cylinders, plates, blankets, and inking systems working in harmony. Modern presses are engineering marvels that can print thousands of sheets per hour while maintaining exceptional quality.
The main components of an offset printing press include:
- Plate cylinder: Holds the aluminum printing plate with the image to be printed
- Blanket cylinder: Covered with a rubber blanket that receives the image from the plate
- Impression cylinder: Applies pressure to press the paper against the blanket
- Inking system: Delivers a controlled amount of ink to the plate
- Dampening system: Applies water to the non-image areas of the plate
- Feeder system: Supplies paper to the press
- Delivery system: Collects and stacks the printed sheets
Investing in an offset printing press requires careful consideration of volume needs and technical capabilities. The size and configuration of an offset printing press determine the types of projects it can handle efficiently. Modern presses often incorporate computer controls, automated plate-changing systems, and inline quality monitoring.
Types of Offset Printing: Sheet-Fed, Web, and Specialty Methods
The main types of offset printing include sheet-fed, web, and waterless offset, each serving different purposes. Understanding the various types of offset printing helps businesses choose the right method for their specific projects.
Sheet-Fed Offset Printing
Sheet-fed presses print on individual sheets of paper fed through the press one at a time. This method offers:
- Greater versatility in paper types and weights
- Higher image quality and registration accuracy
- Better suited for shorter runs and premium print jobs
- Ideal for brochures, posters, and marketing materials
Web Offset Printing
Web offset printing is ideal for newspapers, magazines, and catalogs due to its high-speed production capabilities. This method uses continuous rolls of paper and includes:
- Significantly faster printing speeds
- Lower cost for very high volume runs
- Inline finishing capabilities
- Perfect for newspapers, magazines, catalogs, and books
The continuous paper feed in web offset printing allows for extremely efficient high-volume production. Major publishers rely on web offset printing for consistent quality in their periodicals and books.
Specialty Offset Methods
- Waterless offset: Uses silicone-coated plates instead of the traditional water-based dampening system
- UV offset: Incorporates ultraviolet curing for instant drying
- Perfecting presses: Print both sides of the paper in a single pass
Different types of offset printing offer varying advantages in terms of speed, quality, and material compatibility. The choice depends on project requirements, budget constraints, and quality expectations.
Offset Printing Machine: Equipment Guide and Considerations
Modern offset printing machines incorporate automation and digital controls for improved efficiency. These sophisticated devices range from small single-color presses to massive multi-unit machines capable of printing multiple colors in a single pass.
When selecting an offset printing machine, consider factors like size, color capacity, and automation features. Key considerations include:
- Number of colors: Most commercial presses offer 4-6 color units
- Sheet size capacity: Determines the maximum paper size the press can handle
- Printing speed: Measured in sheets per hour
- Automation level: Features like automatic plate loading and wash-up systems
- Additional capabilities: Inline coating, perfecting, and finishing options
The capabilities of your offset printing machine directly impact the range of services you can offer clients. Advanced machines with computer-to-plate technology, automated color management, and quality control systems produce superior results with less waste and setup time.
Offset Printing Advantages for Commercial Projects
Offset printing offers numerous advantages that make it the preferred choice for many commercial printing projects:
- Superior image quality: Produces sharp and clean images with exceptional detail and color accuracy
- Cost-effective for large runs: As run length increases, the cost per piece decreases significantly
- Material versatility: Works well on various paper types, including specialty stocks and non-paper materials
- Consistent quality: Maintains uniform color and image quality throughout the entire run
- Plate durability: Plates can produce over a million impressions without quality degradation
- Special ink options: Accommodates specialty inks like metallics, Pantone colors, and varnishes
- Precise color matching: Achieves exact color reproduction for brand consistency
When comparing printing methods, offset printing offers superior image quality and cost efficiency for large runs. Many businesses choose offset printing for their marketing materials due to its consistent quality and professional finish.
Offset vs Digital Printing: Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
The decision between offset and digital printing depends on several factors:
For marketing materials requiring exact color matching and high quality, offset printing typically delivers superior results. However, digital printing offers advantages for quick turnaround, variable data, and cost-effectiveness on smaller quantities.
The ideal approach for many businesses is to use both methods strategically: digital for short runs and personalized materials, and offset for larger quantities and premium pieces.
Offset Printing Applications Across Industries
Offset printing serves numerous industries with applications including:
- Publishing: Books, magazines, newspapers, and journals
- Marketing: Brochures, catalogs, direct mail, and promotional materials
- Packaging: Boxes, labels, wrappers, and cartons
- Stationery: Business cards, letterheads, envelopes, and notepads
- Retail: Point-of-sale displays, signage, and promotional materials
- Financial: Annual reports, prospectuses, and financial documents
- Education: Textbooks, workbooks, and educational materials
Each industry benefits from offset printing’s ability to deliver consistent quality at scale. For example, the publishing industry relies on web offset printing for producing millions of books and magazines with consistent quality and reasonable cost.
Commercial Offset Printing Services and Solutions
Commercial offset printing services offer comprehensive solutions for businesses of all sizes. These services typically include:
- Pre-press services: File preparation, color management, and proofing
- Printing options: Various color configurations and specialty techniques
- Finishing services: Cutting, folding, binding, laminating, and special finishes
- Quality control: Color calibration, registration checks, and consistency monitoring
- Logistics: Warehousing, fulfillment, and distribution
When selecting a commercial offset printing provider, consider their equipment capabilities, quality standards, turnaround times, and additional services. Established printers often provide valuable expertise in optimizing designs for the best results.
Modern Offset Printing Technology and Innovations
The offset printing industry continues to evolve with technological advancements:
- Computer-to-plate (CTP) technology: Direct digital plate creation without film
- Automated press controls: Computerized systems for faster setup and reduced waste
- Hybrid offset/digital solutions: Combining the advantages of both technologies
- Environmentally friendly practices: Vegetable-based inks, reduced alcohol content, and waste reduction
- LED-UV curing: Energy-efficient instant drying technology
- Inline finishing: Coating, cutting, and folding in a single production line
- Workflow automation: Integrated systems from file submission to delivery
These innovations have made offset printing more efficient, environmentally friendly, and competitive in the digital age. For example, Heidelberg’s Versafire systems represent the integration of digital capabilities with traditional offset expertise.
Sustainability initiatives in modern offset printing include eco-friendly materials, vegetable-based inks, and energy-efficient systems. These advancements reduce the environmental impact while maintaining the quality advantages of offset printing.
Conclusion
Offset printing remains a cornerstone of the commercial printing industry, offering unmatched quality and cost-effectiveness for medium to large print runs. Its versatility, precision, and reliability make it the preferred choice for projects where quality cannot be compromised.
While digital printing continues to advance, offset printing has evolved through technological innovation to remain relevant and competitive. The integration of digital workflows, automation, and environmental improvements has strengthened offset printing’s position in the modern printing landscape.
For businesses and organizations seeking professional printing results, understanding the capabilities, advantages, and applications of offset printing is essential for making informed decisions. Whether you’re publishing a magazine, creating marketing materials, or producing packaging, offset printing delivers the quality and consistency that helps your products stand out in today’s competitive marketplace.


