The Complete Guide to UV Printing: Technology, Applications & Benefits
UV printing revolutionizes the traditional printing landscape with its ability to instantly cure inks using ultraviolet light. This advanced printing technology delivers exceptional print quality while eliminating drying time, making it a game-changer for modern printing needs.
UV printing technology combines specialized UV-cured inks with innovative UV-LED printing systems to create durable, high-quality prints on virtually any surface. From commercial packaging to industrial applications, this versatile printing method offers significant advantages over conventional printing techniques.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals of UV printing, different technologies available, key applications, and essential benefits. Whether you’re considering implementing UV printing solutions or seeking to understand this technology better, you’ll discover everything you need to know about this cutting-edge printing method.
What is UV Printing?
UV printing stands as a specialized digital printing method that utilizes ultraviolet light to instantly dry or cure ink as it’s applied to various surfaces. Unlike conventional printing processes, UV printing enables immediate solidification of inks through a photochemical reaction, resulting in sharp, vibrant, and durable prints.
Definition and Basic Principles
At its core, UV printing employs specially formulated inks containing photoinitiators that react when exposed to ultraviolet light. This photochemical process triggers a cross-linking chain effect, causing the ink to transform from liquid to solid state almost immediately after application. Originally introduced in the 1960s for curing gel nail polishes, this technology has since evolved into a fundamental printing method across numerous industries.
The basic principle involves a low-temperature, high-speed, solventless process that creates a crosslinked network of polymers through radical or cationic polymerization. This scientific approach enables printing on virtually any material without the lengthy drying times associated with traditional methods.
How UV Printing Works
The UV printing process follows a straightforward sequence of operations:
First, piezo print heads eject specially formulated UV ink with precision onto the substrate. As the printer distributes the ink, high-intensity UV lamps or LED lights positioned beside or behind the printhead follow closely, emitting ultraviolet light at specific wavelengths (typically 200-400nm).
The UV light causes the photoinitiators in the ink to react, triggering an instantaneous polymerization process. This molecular transformation hardens the ink immediately, preventing absorption into the substrate and allowing the ink to remain on the surface with excellent definition and color vibrancy.
Modern UV printing systems often employ LED technology, which offers advantages such as reduced energy consumption, longer lamp life, and lower operating temperatures compared to traditional mercury UV lamps.
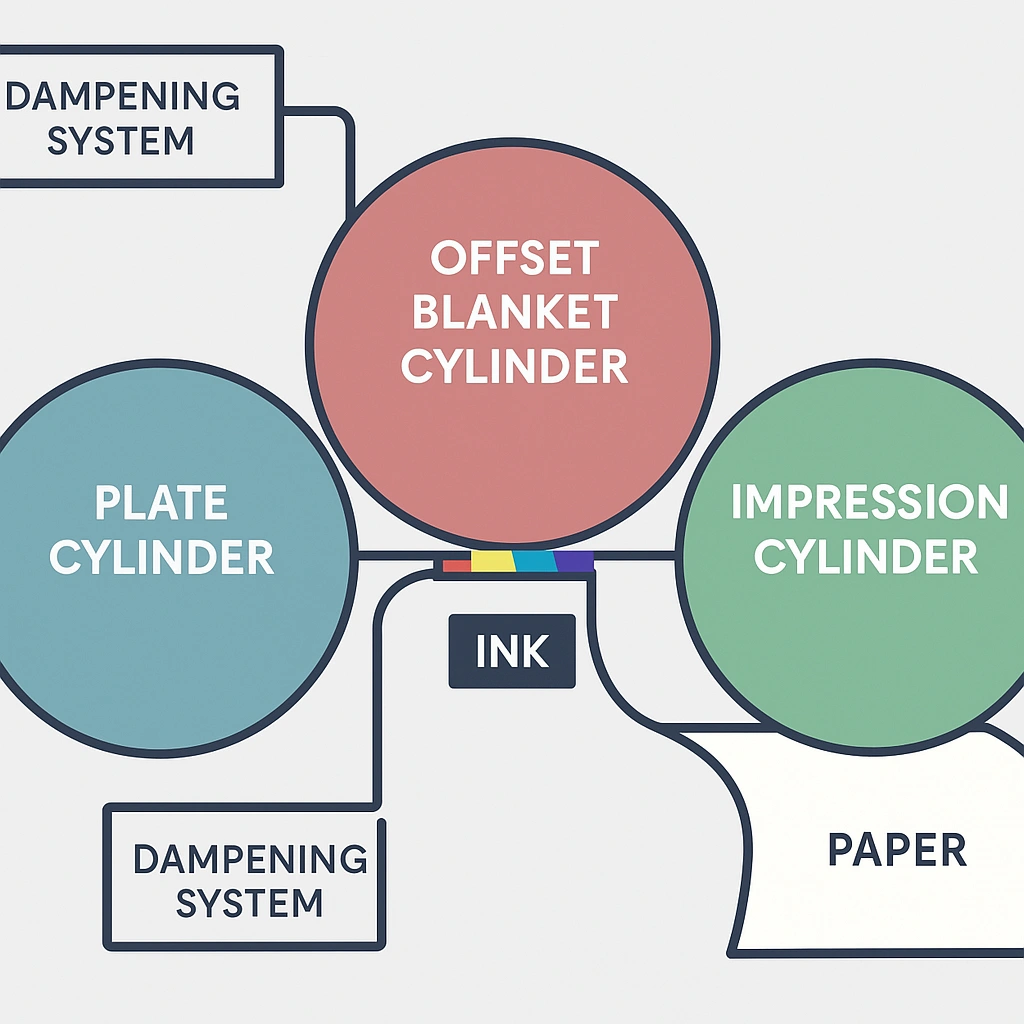
UV vs. Traditional Printing Methods
Traditional printing fundamentally differs from UV printing in several critical aspects:
Traditional printing relies on solvent-based inks that dry through evaporation and absorption. Heat is applied to accelerate this process, which can take hours or even days to complete. Additionally, conventional inks often require spray powders to prevent offsetting and smudging during drying.

In contrast, UV printing offers immediate curing without waiting time. Furthermore, since UV inks don’t need to be absorbed into the substrate, they maintain superior color intensity and definition. Traditional printing is primarily limited to paper and cardboard, whereas UV printing can be applied to virtually any material including plastics, glass, metal, acrylic, and wood.
Traditional methods also release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the evaporation process, making UV printing a more environmentally friendly alternative with almost zero carbon footprint.
Types of UV Printing Technology
The UV printing landscape features several distinct technological approaches, each offering unique advantages for specific applications. Modern UV printing systems have evolved significantly from their early predecessors, primarily focusing on efficiency, versatility, and environmental sustainability.
UV-LED Printing
UV-LED printing represents the cutting edge of ultraviolet curing technology. Unlike traditional systems, LED-based UV printers employ light-emitting diodes that produce focused, unidirectional light at specific wavelengths. These systems offer remarkable efficiency advantages, consuming significantly less power than conventional options.

A standout feature of UV-LED technology is its exceptional durability—with lamps typically lasting for 10,000 hours or up to five years of regular use. Consequently, these systems require minimal maintenance throughout a printer’s lifetime. Most notably, LED lamps operate with instant on/off capability without degradation of intensity, eliminating warm-up time and boosting operational efficiency.
The reduced heat output of LED systems provides additional benefits, allowing printing on heat-sensitive materials like thin slides, self-adhesive sheets, and stretched PVC that would otherwise warp or damage under traditional lamps. Moreover, the cooler operation ensures stable media positioning beneath the print shuttle, reducing head crashes and material waste.
UV-Cured Printing
Traditional UV-cured printing relies on mercury vapor lamps operating across a wider UV spectrum. This established technology was the foundation of early UV printing systems before LED innovations entered the market.
Mercury-based systems generate a broader UV wavelength range, which can offer advantages for certain ink formulations. However, these lamps typically have shorter lifespans than their LED counterparts and generate more heat during operation.
The thermal output necessitates additional cooling systems and limits usage with heat-sensitive substrates. Furthermore, mercury vapor lamps require disposal protocols due to their mercury content, creating additional environmental considerations.
Hybrid UV Systems
Hybrid UV technology combines the versatility of different printing approaches in a single machine. These systems integrate flatbed and roll-to-roll capabilities, allowing operators to switch between printing on rigid and flexible materials without changing equipment.
This versatility makes hybrid systems particularly valuable for print shops handling diverse projects. A hybrid UV printer can process both flat materials like acrylic, wood, and glass alongside flexible substrates such as vinyl, fabric, and paper.
Modern hybrid UV printers often feature advanced capabilities like white ink printing and variable dot technology. Some incorporate Kyocera printheads with 2,656 nozzles, delivering exceptional resolution and vibrant colors across multiple material types.
Applications of UV Printing
The extensive versatility of UV printing spans multiple industries, offering solutions for diverse production needs. This technology has been in use for over thirty years, with UV-LED systems now rapidly becoming the new standard across numerous applications.
Commercial Printing
Commercial printing benefits greatly from UV printing’s ability to produce eye-catching, durable signage for both indoor and outdoor use. The technology creates vibrant window displays and in-store promotions that effectively attract customers. For advertising professionals, UV printing delivers exceptional print quality—the instant drying time results in sharp, detailed prints ideal for creating point-of-purchase displays, exhibition graphics, and promotional materials. First and foremost, the precision of UV printing ensures that even the smallest textual elements and intricate designs are accurately reproduced, making it essential for high-impact commercial applications.
Packaging and Labels
In the packaging sector, UV printing plays a crucial role where product presentation and branding are essential. This technology enables companies to print high-definition graphics and logos directly onto various packaging materials including cardboard, plastic, and glass. Remarkably, UV printing creates labels with raised textures and unique finishes that enhance product appeal. The quick curing process makes it suitable for high-speed production lines, improving efficiency in packaging manufacturing. Indeed, UV-LED technology for flexographic printing provides faster throughput and higher yield through tighter process control, allowing the use of thinner and heat-sensitive materials.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, UV printing serves both functional and esthetic purposes. Manufacturers utilize this technology to mark serial numbers, barcodes, and QR codes directly onto machine parts, circuit boards, and electronic devices. The technology’s precision ensures accurate reproduction of critical information on components. Subsequently, UV printing enhances control panel overlays with high accuracy, allowing complex designs and detailed labels to be printed on various overlay materials. The medical sector also benefits, as UV printing enables precise customization on medical devices, ensuring each device meets exacting standards.
Specialty and Custom Printing
UV printing excels in creating personalized merchandise and promotional products. Accordingly, items that can be customized include:
- Phone cases, pens, USB drives, and keychains with detailed designs
- Decorative panels, custom tiles, and furniture with textured effects
- Glass and ceramic surfaces with intricate, water-resistant designs
- Sports equipment including golf balls and hockey pucks
To demonstrate its versatility, UV printing technology can apply customization directly onto curved and irregular surfaces, making it ideal for producing high-quality promotional goods. In essence, this capability has transformed industries ranging from home décor to fashion, allowing businesses to offer unique, personalized products with exceptional durability.
Benefits of UV Printing
The advantages of UV printing extend far beyond its impressive applications, offering tangible benefits across multiple dimensions. From environmental sustainability to enhanced print quality, this technology provides comprehensive improvements over traditional printing methods.
Environmental Advantages
First and foremost, UV printing technology stands out for its eco-friendly characteristics. Unlike solvent-based printing methods, UV inks emit negligible volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and produce no hazardous air pollutants during curing, creating a healthier workplace environment. Primarily, the UV curing process eliminates the need for solvents, making it an environmentally responsible choice.
The energy efficiency of UV-LED systems further enhances the environmental profile of this technology. LED lamps consume less power than traditional mercury bulbs, leading to substantial energy savings and higher return on investment. Essentially, these lamps require no warm-up time and can be switched on and off instantly, reducing standby power consumption.
Another environmental benefit comes from reduced waste generation. Because UV inks don’t evaporate during printing, less ink is wasted throughout the process. Plus, the absence of mercury in LED systems eliminates disposal concerns and associated costs.
Print Quality and Durability
UV printing delivers exceptional print quality with vibrant colors and sharp images. The instant curing process prevents ink absorption into the substrate, resulting in more precise details and superior color saturation.
In terms of longevity, UV-printed materials exhibit remarkable durability:
- Resistance to fading for at least 2 years, extended further with lamination
- Superior protection against water damage and scratching
- Enhanced resistance to wear and weathering
Production Efficiency
The instant curing capability of UV printing dramatically improves production workflows. With no drying time required, printed materials can be immediately handled and finished, increasing throughput and meeting tight deadlines. This immediate processing allows businesses to complete more jobs in less time, boosting overall productivity.
Material Versatility
Finally, UV printing excels in material compatibility. Given that UV inks cure instantly without being absorbed, they don’t etch, damage, or react with the media. Likewise, the low curing temperatures permit printing on heat-sensitive materials that would otherwise warp under traditional heating methods. This versatility enables printing on nearly any flat surface—including wood, glass, PVC, acrylic, plastic, stone, and leather—expanding creative possibilities.
UV Printing Equipment
Modern UV printing equipment combines precision engineering with advanced technology to deliver exceptional print quality across various materials. The selection of appropriate hardware greatly influences production capabilities and output quality.
Printers and Presses
UV printing hardware ranges from compact desktop units to industrial-scale production systems. Flatbed UV printers dominate the market, offering direct printing on rigid materials up to 3.94 inches thick. These machines vary in print area capacity—from small-format desktop printers like the BD-8 VersaSTUDIO (210 x 148 mm) to large industrial models such as the CO-i Series (1,612 × 3,050 mm). Primarily, cylindrical UV printers serve specialized applications, enabling decoration of curved surfaces.
Many contemporary systems feature touchscreen interfaces, automatic thickness detection, and multi-zone vacuum systems that hold materials securely without taping. High-end models incorporate staggered printheads for increased production speed alongside precision positioning systems.
UV Lamps and LED Systems
Two main curing technologies power UV printing systems:
- Mercury lamps: Traditional UV curing uses mercury vapor lamps that emit across a broader UV spectrum. Although effective, these systems generate more heat and require proper disposal protocols.
- LED lamps: Modern UV-LED systems provide several advantages—they’re ozone-free, energy-efficient, and long-lasting (typically 10,000+ hours). Initially, these systems operate at lower temperatures, making them suitable for heat-sensitive materials while consuming less power than conventional alternatives.
Inks and Coatings
UV-curable inks contain photoinitiators, monomers, polymers, and oligomers that solidify when exposed to UV light. Formulations typically include:
- CMYK process colors for standard printing
- White ink for printing on dark or transparent surfaces
- Varnish for creating textured effects and protective finishes
- Specialty inks including red, orange, and gray for expanded color gamut
Most importantly, these inks offer exceptional adhesion to various substrates including plastic, glass, metal, and wood. Many formulations provide scratch resistance, high surface gloss, and excellent opacity.
Maintenance Requirements
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of UV printing equipment. Essential practices include:
- Daily printhead cleaning to prevent clogging and ensure consistent quality
- Regular UV lamp cleaning to maintain proper curing performance
- Thorough cleaning of the work area and print bed to prevent dust contamination
- Periodic inspection of vacuum systems and mechanical components
- Software and firmware updates to enhance functionality
Routine maintenance schedules typically include daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly tasks. Following manufacturer-recommended procedures significantly reduces downtime and extends equipment life.
Considerations When Choosing UV Printing
Selecting the right UV printing solution demands thoughtful analysis of several critical factors. Prior investment in research can prevent costly mistakes and ensure optimal results for your specific needs.
Cost Analysis
Evaluating UV printing costs requires looking beyond the initial purchase price. UV printers range from $4,000 for basic models to $85,000 for advanced systems. Alongside upfront expenses, factor in ongoing operating costs—UV inks typically cost $28-35 per liter, with maintenance requiring approximately 8ml of ink per cleaning cycle at $0.30 per ml. Electricity consumption adds roughly $0.06 per square meter to overall costs. The total printing cost generally falls between $1.25-$1.44 per square meter. ROI calculators can help determine if this investment aligns with your business objectives.
Space and Ventilation Requirements
UV printers demand adequate physical space—typically a minimum area of 6 feet x 6 feet. Proper clearance is essential: at least 20 inches from back walls and 12 inches from sides to enable maintenance access. Despite producing fewer emissions than traditional printing methods, ventilation remains crucial. Options include dedicated ventilation systems, inline fans with hoses directed outdoors, or air scrubbers with HEPA and activated carbon filters. The optimal operating environment maintains temperature between 68-77°F with humidity levels of 35-70%.
Training and Expertise
Operating UV equipment requires specialized knowledge spanning machine operation, software proficiency, and maintenance protocols. Comprehensive training options include manufacturer-provided programs, industry workshops, online courses, and hands-on instruction. Well-trained operators improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and produce higher quality prints. Understanding safety protocols for UV exposure is equally important.
Material Compatibility
Material selection significantly impacts print quality and durability. Consider surface texture—smooth materials like glass provide excellent ink adhesion, yet textured surfaces may require pre-treatment. Material thickness and rigidity affect printer bed adjustments. Always evaluate the substrate’s intended purpose, as different materials offer varying levels of weather resistance and durability.
Future Trends in UV Printing
The UV printing industry stands at the cusp of remarkable evolution, with projections indicating growth to USD 89.25 billion by 2029 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.2%. This expansion represents a significant shift in both technological capabilities and market applications.
Technological Advancements
Intelligent automation represents a cornerstone of UV printing’s future. By 2025, UV printing equipment will no longer function as standalone tools but rather as integrated components of entire production lines. The deep integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies promises to drive comprehensive upgrades throughout production processes. For instance, AI combined with UV printing technology will automate everything from file processing to post-processing. Most importantly, these smart systems will reduce human intervention, increasing both production efficiency and accuracy while minimizing errors.
Printhead technology is undergoing significant innovation as well. New advancements will dramatically increase printing speeds, with some systems achieving 2-3 times faster output than current models. These high-speed capabilities will be complemented by ultra-high precision printing with resolutions of 1200dpi and above. Rather than sacrificing quality for speed, these technologies deliver both simultaneously.
Market Growth Areas
Personalized customization represents a booming market opportunity. From mobile phone cases and home decor to car interiors and fashion accessories, consumer demand for unique products continues to surge. Small-batch, diverse production runs perfectly align with UV printing’s strengths. In addition, UV printing will increasingly cross boundaries with other industries, creating novel application scenarios such as personalized decorative walls that provide unique artistic experiences.
The packaging industry specifically drives significant growth, with UV inkjet printing offering high-quality, versatile, and sustainable solutions. This sector values UV printing’s ability to enhance efficiency, quality, and sustainability while meeting modern consumer demands.
Sustainability Developments
Environmental responsibility is transforming from an optional feature to an essential requirement across the UV printing industry. First and foremost, green technology will become a core competitive advantage by 2025. UV-LED inks are gradually replacing traditional solvent-based inks with their volatile organic compounds (VOCs), offering lower energy consumption, faster curing speeds, and reduced harmful emissions.
The industry is simultaneously pursuing bio-based and renewable materials for UV-cured inks. This focus on eco-friendly formulations will further reduce the environmental footprint of UV printing. In fact, some manufacturers are developing UV inks with more than 40% renewable and vegetable-based components—four times higher than standard UV offset inks.
Conclusion
UV printing stands as a transformative technology that combines exceptional print quality with environmental responsibility. Through advanced UV-LED systems, instant curing capabilities, and remarkable substrate versatility, this printing method delivers significant advantages over traditional approaches.
The technology excels across multiple sectors – from commercial printing and packaging to industrial applications and custom merchandise. These capabilities, paired with notable benefits like zero VOC emissions, superior durability, and enhanced production efficiency, position UV printing as a leading solution for modern printing needs.
Looking ahead, UV printing continues to evolve with smart automation, AI integration, and sustainable innovations. Market projections suggest substantial growth, especially in personalized products and packaging solutions. Additionally, emerging eco-friendly ink formulations and energy-efficient systems demonstrate the industry’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
This comprehensive printing solution offers businesses a practical path toward efficient, high-quality output while maintaining environmental responsibility. The technology’s ongoing advancement, coupled with its proven track record, establishes UV printing as an essential tool for meeting current and future printing demands.
The Complete Guide to UV Printing: Technology, Applications & Benefits Read More »